Introduction
Hyperlipidemia affects a significant portion of U.S. adults. According to the CDC, about 86 million Americans aged 20 and older have total cholesterol levels above 200 mg/dL, and nearly 25 million have high cholesterol above 240 mg/dL. Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of death in the U.S., claiming 680,981 lives in 2021, with a death rate of 203.3 per 100,000. In internal medicine, hyperlipidemia is commonly managed often alongside other chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension to reduce this risk.
In internal medicine, hyperlipidemia is one of the most frequently managed chronic conditions and often coexists with diabetes, hypertension, and obesity.
This comprehensive guide will help you:
- Understand what ICD-10 Code E78.5 really means
- Use it correctly with co-existing chronic conditions
- Improve documentation and avoid common coding errors
- Stay compliant while optimizing revenue
What Is Hyperlipidemia?
Hyperlipidemia refers to abnormally high levels of lipids (fats) in the blood, primarily cholesterol and triglycerides. These lipids are essential for various body functions, but when their levels become too high, they can accumulate in the walls of arteries and form plaques, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis, heart attack, and stroke.
There are different types of hyperlipidemia, including:
- Hypercholesterolemia – high cholesterol levels (especially LDL or “bad” cholesterol)
- Hypertriglyceridemia – elevated triglyceride levels
- Mixed hyperlipidemia – elevated cholesterol and triglycerides
In many cases, hyperlipidemia has no symptoms and is only detected through routine blood tests. It is often linked to poor diet, lack of exercise, obesity, smoking, diabetes, or genetic conditions like familial hypercholesterolemia.
Because it's a silent but serious risk factor for cardiovascular disease, early diagnosis, ongoing monitoring, and proper coding like ICD-10 Code E78.5 are essential in internal medicine to guide treatment and prevent complications.
What Is the ICD-10 Code For Hyperlipidemia?
ICD-10 Code E78.5 stands for hyperlipidemia, unspecified, and is categorized under E78 Disorders of lipoprotein metabolism and other lipidemias.
Code Breakdown: (Table)
Code | Description |
E78.0 | Pure hypercholesterolemia |
E78.1 | Pure hyperglyceridemia |
E78.2 | Mixed hyperlipidemia |
E78.5 | Unspecified hyperlipidemia |
Use ICD-10 Code E78.5 only when the provider does not specify the lipid type (e.g., LDL, HDL, triglycerides) or when the documentation simply states “hyperlipidemia” or “high cholesterol” without details.
Why Hyperlipidemia Matters in Internal Medicine
Hyperlipidemia isn't just a lab value it’s a chronic condition that demands ongoing care. It contributes to increased risk of stroke, heart attacks, peripheral artery disease, and renal complications.
In the internal medicine setting, it's often managed alongside:
- Type 2 diabetes (E11 series)
- Essential hypertension (I10)
- Obesity (E66.x)
- Coronary artery disease (I25.10)
Providers typically prescribe statins, recommend lifestyle changes, and monitor lab values to reduce cardiovascular risk. Accurate coding ensures appropriate reimbursement, patient risk profiling, and care planning.
When to Use Hyperlipidemia (E78.5) With Other Chronic Conditions
1. Combining Hyperlipidemia (E78.5) with Diabetes (E11 Series)
Patients with diabetes commonly have lipid abnormalities. If both conditions are documented separately (e.g., “Type 2 diabetes” and “hyperlipidemia”), assign both E11.9 and E78.5.
Do NOT use E78.5 if the provider specifies “diabetic dyslipidemia” or “hyperlipidemia secondary to diabetes.” In that case, use a combination code or query the provider.
2. Combining Hyperlipidemia (E78.5) with Hypertension (I10)
Many patients present with both elevated blood pressure and lipids. When documented, use I10 and E78.5 separately unless the provider links them.
Key Tip: Don’t assume relationships between conditions. Always follow the provider's documentation.
Key Documentation Requirements for Hyperlipidemia (E78.5)
To correctly assign E78.5, documentation must align with ICD-10 coding rules not just lab results. The provider's note should reflect the diagnosis clearly and avoid assumptions. Below are the key documentation elements coders should verify before using this code:
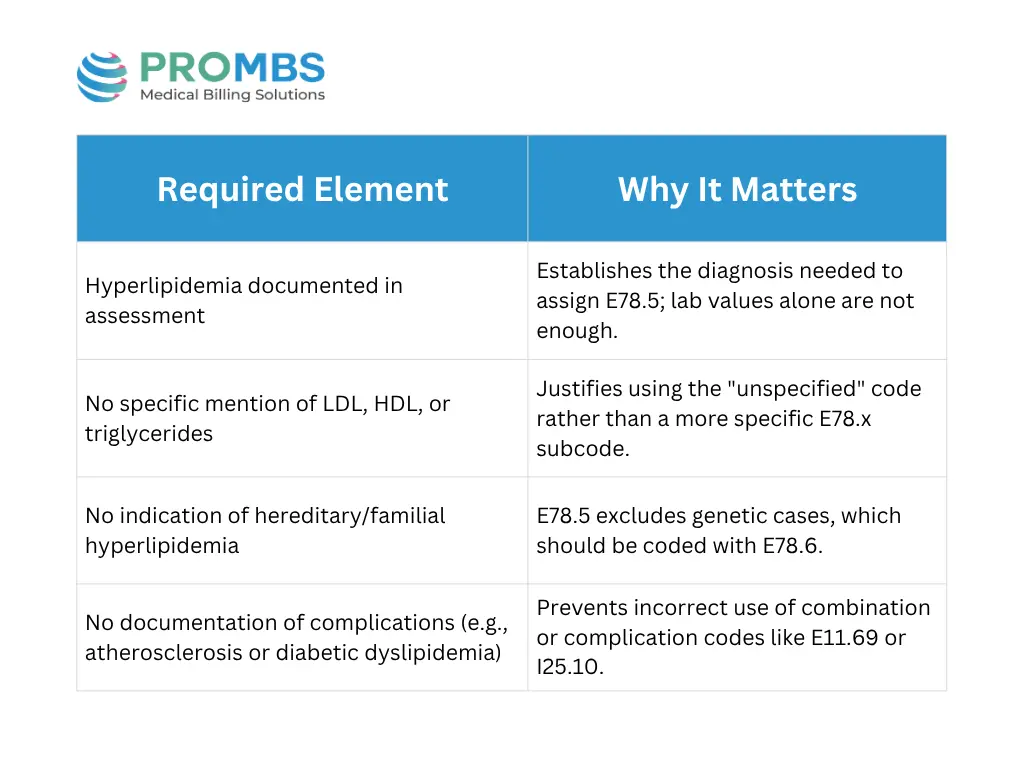
Even if labs suggest a specific lipid abnormality, coders must rely on the provider’s written assessment. If the provider documents terms like “elevated LDL” or “familial hypercholesterolemia,” a more specific code such as ICD-10 code E78.0 or ICD-10 code E78.6 should be used instead of ICD-10 code E78.5.
Why Chronic Disease Coding Accuracy Matters
ICD-10 code E78.5 is often used in Medicare Advantage and value-based care models where risk adjustment affects payment. If hyperlipidemia is under coded or not documented, it can:
- Undermine patient risk profiles
- Affect HCC scores
- Lead to lost reimbursement
- Reduce care plan accuracy
Use ICD-10 code E78.5 accurately with coexisting codes like:
- ICD-10 code E11.9 – Type 2 diabetes without complications
- ICD-10 code I10 – Hypertension
- ICD-10 code E66.9 – Obesity, unspecified
- ICD-10 code I25.10 – Atherosclerotic heart disease
Common Coding Mistakes to Avoid
Mistake | Explanation | Fix |
Defaulting to E78.5 when LDL or triglycerides are documented | Leads to underreporting | Use E78.0 or E78.1 if specified |
Ignoring provider-patient discussions in assessment | Important for diagnosis validation | Encourage complete documentation |
Not updating code when lipid status improves or changes | Outdated diagnosis = denial risk | Reflect current condition per visit |
Clinical Case Example: Correct vs Incorrect Use
A 56-year-old male presents for an annual exam. His labs show elevated LDL and triglycerides. The provider’s note states only: “hyperlipidemia, continue statin.”
- Incorrect Code: E78.0 – Pure hypercholesterolemia (not supported by documentation)
- Correct Code: E78.5 – Unspecified hyperlipidemia (matches provider’s note)
Now suppose the provider had documented: “LDL elevated, diagnosed with pure hypercholesterolemia.”
- Correct Code: E78.0 – Pure hypercholesterolemia
Lesson: You must follow the provider’s language—not lab results alone—when assigning codes. Accurate documentation is key to coding specificity.
Tips for Coding Hyperlipidemia (E78.5) More Accurately
- Query the provider if labs indicate specific lipid issues
- Encourage documentation that references LDL, HDL, and triglycerides
- Always update the diagnosis when the clinical picture changes
- Use EHR alerts to flag missing specificity in assessments
Why Partner With Pro-MBS for Internal Medicine Billing
Hyperlipidemia coding might seem routine, but it's a critical aspect of chronic care management and internal medical billing.
Our Pro-MBS billing experts specialize in streamlining hyperlipidemia coding and improving accuracy in chronic care billing.
- Flag missed opportunities in lipid disorder coding
- Educate providers on clinical documentation improvement (CDI)
- Reduce denials from unspecified codes
- Align coding with value-based payment models
- Optimize annual wellness and chronic care billing
Whether you're managing a solo practice or a multi-provider internal medicine group, we make sure your chronic condition billing is accurate, clean, and optimized.
Conclusion
While ICD-10 code E78.5 may appear to be a convenient catch-all code, using it correctly requires precision and clinical insight. It plays an important role in documenting hyperlipidemia when the specific lipid abnormality isn’t detailed in the provider's notes but it should never be used by default. When applied properly, this code can help reflect the true complexity of a patient’s condition, ensure accurate HCC risk adjustment, and support full reimbursement. However, relying on it without clear documentation or when more specific information is available can lead to coding errors, denials, and compliance concerns. The key lies in consistent, thorough documentation, strong communication between coders and providers, and regular updates to the diagnosis based on the most current clinical findings. ICD-10 code E78.5 is a valuable part of your coding toolkit just make sure it's used with purpose and precision.



