Ambulatory Surgical Centers (ASCs) have become a preferred setting for many outpatient procedures due to their efficiency, lower costs, and quicker turnaround times. However, billing for these services isn’t the same as billing for hospital-based procedures. Ambulatory surgical center billing follows its own set of rules, and understanding these differences is critical for clean claims and faster reimbursements.
Whether you're a solo practitioner, part of a multi-specialty group, or managing billing for an ASC, this guide will help you understand the essentials of ambulatory surgical center billing and how it stands apart from traditional medical billing.
What Is an Ambulatory Surgical Center in Medical Billing?
An ambulatory surgical center is a healthcare facility that offers same-day surgical care without the need for hospital admission. These centers are typically equipped to handle diagnostic and preventive procedures that do not require extended recovery time.
In medical billing, an ambulatory surgical center refers to both the location and the billing structure associated with these outpatient services. The coding, payer rules, and reimbursement models can differ significantly from those used in physician offices or hospitals.
Key Elements of Ambulatory Surgical Center Billing
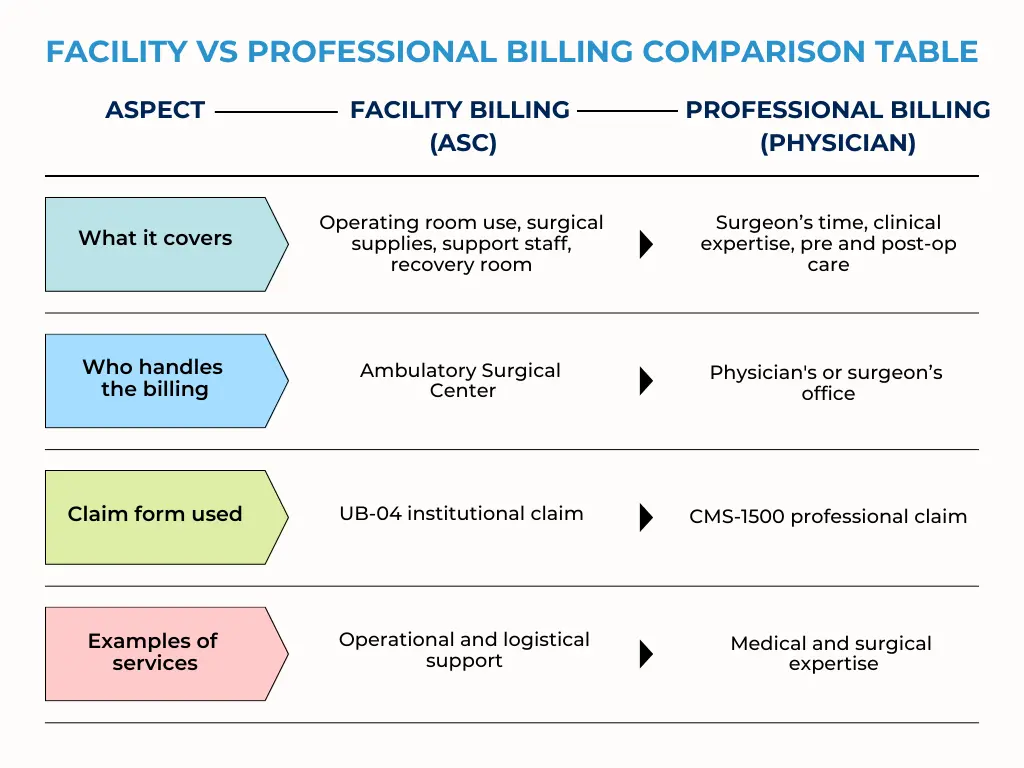
1. Facility vs. Professional Billing
What’s the Difference
Professional billing refers to the care provided by the physician or surgeon. This includes examining the patient, performing the procedure, and offering post-operative follow-up. These services are billed by the physician’s office using the CMS-1500 form.
Facility billing refers to the resources and services provided by the ASC itself. This includes the use of the operating room, recovery area, medical supplies, and support staff. These charges are billed by the ASC using the UB-04 institutional claim form.
In most cases, ASCs handle only the facility billing. The professional billing is managed separately by the physician’s billing team to ensure clean claims and avoid duplication.
2. Approved Procedures and Payers
When your healthcare provider recommends a service or medication that requires prior authorization, they submit a request to your insurance company. This request typically includes details about your diagnosis, treatment plan, and medical history.
Step 2 Insurance Company Reviews the Request
Not every procedure can be performed or reimbursed in an ASC setting. Medicare and commercial payers have specific lists of approved methods. For example, Medicare maintains an ASC-covered procedures list, which is updated annually.
Before billing, always verify that:
- The procedure is on the payer’s approved list.
- The ASC is credentialed and in-network with the insurance plan.
3. Unique Coding Guidelines
- CPT and HCPCS Level II codes for procedures and supplies.
- Revenue codes to categorize services (like OR use, recovery, or anesthesia).
- Modifiers to give context (e.g., multiple procedures, discontinued procedures).
4. Bundling and Unbundling Rules
5. Payment Methodologies
ASCs are reimbursed differently from hospitals. Medicare, for instance, uses a prospective payment system specific to ASCs. Commercial payers may follow a fee schedule, a percentage of charges, or negotiated contract rates.
Understanding each payer’s methodology can prevent confusion and improve collections.
How ASC Billing Differs from Hospital Billing
Setting of Care
Reimbursement Rates
Billing Codes and Guidelines
Licensing and Certification
To qualify for reimbursement, ASCs must be properly certified by Medicare or accredited by organizations like AAAHC or The Joint Commission. Billing is only valid when the center meets these standards.
Best Practices for Ambulatory Surgical Center Billing
To improve collections and minimize denials, follow these proven ASC billing strategies:
Pre-Authorization Checks
Always obtain prior authorization from payers. This includes confirming coverage, verifying patient eligibility, and ensuring the procedure is on the ASC’s covered list.
Accurate Coding and Documentation
Ensure coders are up to date on CPT and HCPCS codes specific to ASCs. Surgeons should provide clear documentation that supports medical necessity and includes operative notes.
Claim Scrubbing and Validation
Use billing software or third-party services to scrub claims for errors before submission. Validation tools help reduce rejections and improve first-pass acceptance rates.
Timely Filing and Follow-Up
Stay Updated on Regulatory Changes
ASC billing guidelines evolve regularly, especially with Medicare and Medicaid. Subscribe to payer updates and professional newsletters to stay informed.
Partnering With the Right Billing Experts
Ambulatory surgical center medical billing is highly specialized. Partnering with a billing service that understands the intricacies of ASC billing can make a big difference in performance. From coding accuracy to payer negotiations and denial management, expert support ensures compliance and maximizes reimbursement.
We help Ambulatory surgical centers streamline their billing with proven workflows, expert coders, and responsive support teams. Whether you're launching a new center or looking to optimize your current process, we can help you manage ASC billing with confidence.
Final Thoughts
Ambulatory surgical center billing may seem complex, but with the right knowledge and tools, it can become a smooth and efficient process. Understanding how ASC billing differs from traditional facility billing is the first step to ensuring clean claims, reducing denials, and improving cash flow.
By staying informed, applying best practices, and partnering with experts, providers can take full advantage of the ASC model without the usual billing headaches.