Shortness of Breath ICD 10 uses code R06.02. This code applies when a patient has trouble breathing and the provider has no confirmed diagnosis during the visit.
Shortness of Breath ICD 10 is a common reason people go to the doctor. Clinics and hospitals see it every day. Wrong coding causes claim denials. It also slows payments.
In the United States, medical care teams see shortness of breath often. Doctors and staff manage these visits each day. Poor coding creates problems fast. Claims stop, and payments take longer.
This guide explains ICD 10 shortness of breath. It shows when to use code R06.02 and when not to use it. It helps you code the right way and avoid billing problems.
What Does Shortness of Breath ICD 10 Mean in Medical Coding?
Shortness of breath means a patient feels they cannot get enough air. Providers also call it dyspnea. Patients describe chest tightness, fast breathing, or air hunger. These are clear signs and symptoms of abnormalities of breathing.
Clinically, shortness of breath may be:
- Acute (asthma, pneumonia, pulmonary embolism)
- Long-term (COPD, heart failure)
- With activity or at rest
- Mild or a medical emergency
Providers evaluate this symptom using a physical exam, patient medical history, and testing. These include oxygen readings, labs that measure oxygen and carbon dioxide, and imaging such as a chest x ray. These steps help assess lung functioning, blood flow, and overall stability.
For coding, details matter. ICD-10-CM rules say to use the best diagnosis code from the notes. If the provider names the cause, coders must code that cause, not the symptom.
Which ICD-10 Code Should You Use for Shortness of Breath?
Shortness of Breath ICD 10 coding depends on clear provider notes. Each code fits a different clinical situation. Using the wrong code can affect payment and review. The table below lists the primary ICD-10 codes and when to use each one.
| ICD-10 Code | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| R06.02 | Shortness of breath | Used when SOB is documented without a confirmed underlying diagnosis |
| R06.00 | Dyspnea, unspecified | Use only if the provider has documented "dyspnea" but no further qualifiers |
| R06.09 | Other forms of dyspnea | Use for specified dyspnea types not covered by R06.02 |
| R06.03 | Acute respiratory distress | Use if clearly documented as such |
| R06.01 | Orthopnea | SOB when lying flat |
Important:
If documentation confirms a definitive diagnosis such as asthma, heart failure, or pulmonary embolism, code that condition first. Do not rely on ICD 10 for shortness of breath alone.
When Is R06.02 the Correct ICD-10-CM Code?
Use R06.02 only when shortness of breath stands alone as a symptom. The provider must not identify the cause yet.
This ICD-10-CM code falls under the chapter: Symptoms, signs, and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings not elsewhere classified.
R06.02 is a 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 2026 billable specific code, so payers still accept it when used correctly.
Do not use ICD 10 code for short of breath when documentation supports:
- Respiratory distress with defined criteria
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome or respiratory distress syndrome ARDS
- Respiratory failure, especially when the patient needs a mechanical ventilator
- A confirmed disease process
Using R06.02 in these cases weakens medical necessity and increases audit risk.
What Documentation Is Required for Shortness of Breath ICD 10?
Accurate coding depends on strong provider notes. For Shortness of Breath, ICD 10 Documentation should include:
- Onset and duration
- Triggers and risk factors
- Related signs and symptoms
- Oxygen readings and the level of oxygen
- Test results such as chest X-ray
- Response to oxygen therapy
- Relevant medical history
Strong documentation example:
“Patient reports acute shortness of breath on exertion for two days. Oxygen saturation 88% on room air. Improved with oxygen therapy. No chest pain. Chest X-ray ordered. Differential includes pneumonia versus COPD.”
This level of detail supports correct code selection and protects claims during medical review.
What Are Common Coding Errors with R06.02?
Shortness of Breath ICD 10 coding looks simple, but mistakes happen often. Small errors with R06.02 can delay payment or cause denials. Most issues start when documentation lacks clear detail.
The table below shows the most common coding mistakes and their impact.
| Error | Impact |
|---|---|
| Using R06.02 when a more specific diagnosis is available | Leads to unspecified coding and potential denials |
| Coding both R06.02 and a definitive diagnosis without medical necessity | May cause redundancy or trigger payer edits |
| Failing to code comorbidities like COPD or CHF that explain SOB | Missed DRG optimization and risk adjustment |
| Omitting objective clinical evidence (O₂ saturation, ABGs) in notes | Increases denial risk during medical review |
| Confusing R06.02 with codes for respiratory failure | Could misrepresent severity and alter DRG |
Pro Tip :
Always decide whether shortness of breath is the main reason for care or a symptom of another medical condition.
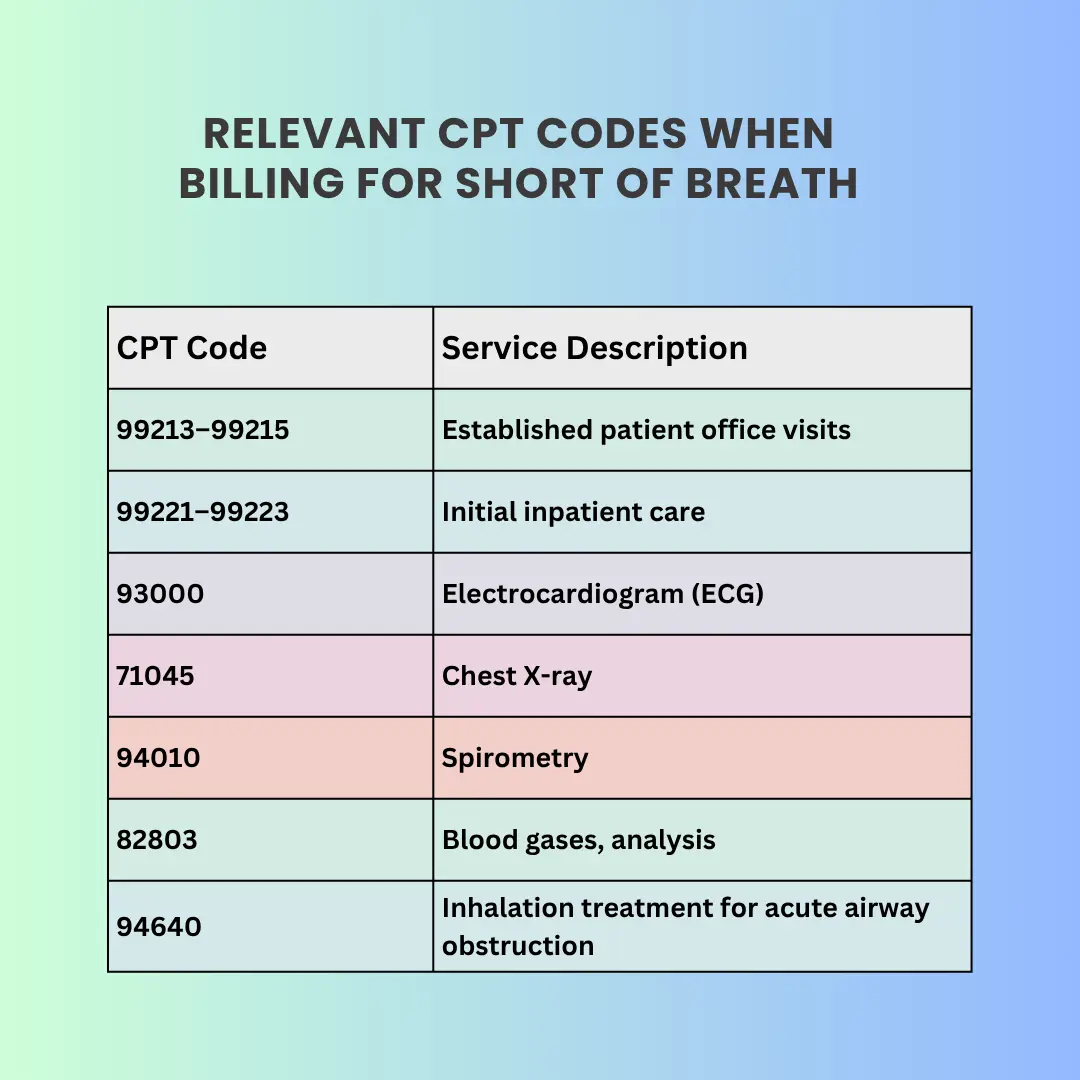
CPT Coding and Payer Expectations
R06.02 supports evaluation and diagnostic services for Shortness of Breath ICD 10 cases. CPT codes must match the work performed and clearly show medical necessity.
Payer expectations include:
- Medicare: Reviews symptom-only claims closely
- Commercial payers: Expect testing, imaging, or follow-up
- Risk adjustment: Symptom codes alone rarely affect scoring
When shortness of breath links to conditions that affect blood flow, oxygen exchange, or cardiac output, coders must capture those diagnoses to support risk adjustment.
When NOT to Use R06.02
Do not use this ICD-10 code when:
- A confirmed cause explains the symptom
- Documentation states acute respiratory distress
- The case meets criteria for respiratory failure
- Ventilator support is required
- A post-surgical or injury code applies
Incorrect use can misstate severity and lead to denial.
How Is R06.02 Different from Other Dyspnea Codes?
R06.02 applies only to shortness of breath without a known cause.
Use R06.09 other forms of dyspnea when documentation specifies a different dyspnea type. Avoid overlap with respiratory distress or acute respiratory distress syndrome unless the criteria clearly apply.

How Pro-MBS Protects SOB Coding Accuracy
Pro-MBS checks clinical notes for missing details. We make sure notes are clear and complete. Our team looks at exam notes, oxygen numbers, and test results. We also confirm what the provider meant. We apply payer rules to every ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code like r06.02 diagnosis code.
We check that diagnosis codes match the service. If something is not clear, we ask the provider. This helps claims follow the rules and get paid faster.