What Is Left Arm Pain and Its Symptoms?
Left arm pain may be localized or radiating from underlying conditions such as musculoskeletal strain, nerve compression, vascular issues, or even cardiac events. Typical symptoms include:
- Dull, aching pain in the upper or lower arm
- Tingling or numbness
- Pain aggravated by movement or exertion
- Referred pain from cervical spine or cardiac origins
Correctly linking these clinical presentations to the left arm pain ICD 10 code helps establish medical necessity and ensures accurate claim submission.
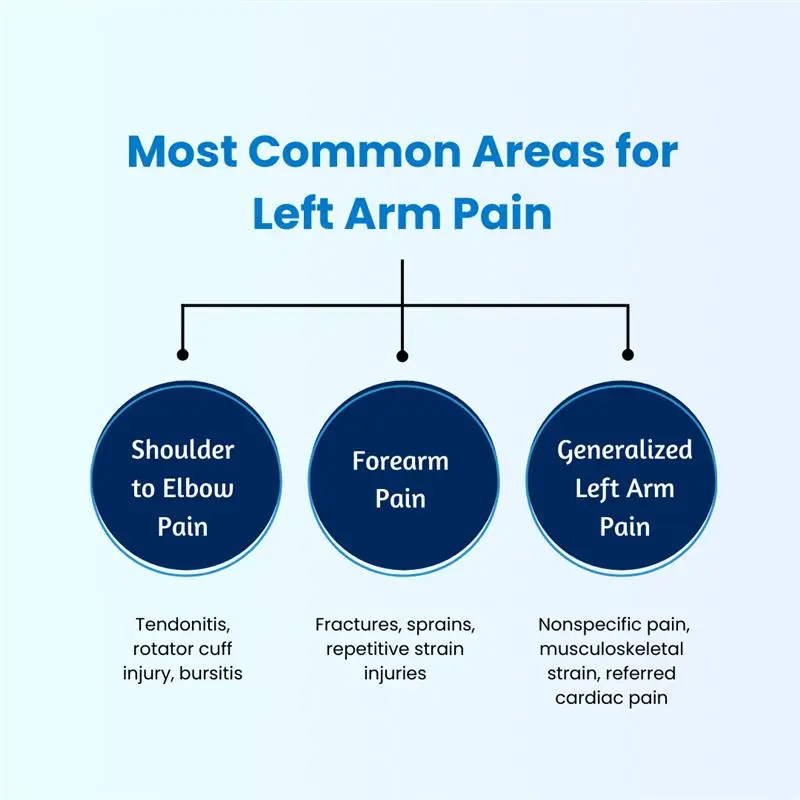
What Is the ICD-10 Code for Left Arm Pain?
The official ICD-10 code for left arm pain is:
M79.602 – Pain in left arm
This code falls under “Other soft tissue disorders, not elsewhere classified” and is used when documentation clearly specifies pain localized to the left arm but without a definitive etiology.
Related ICD-10 Codes
Other codes frequently used in relation to left arm pain include:
| Code | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| M79.602 | Pain in left arm | Primary code for nonspecific left arm pain without confirmed cause |
| M79.601 | Pain in right arm | When pain is localized to the right arm |
| M79.603 | Pain in arm, unspecified | When laterality (left vs. right) is not documented |
| M25.512 | Pain in left shoulder | Use when pain is specifically documented in the left shoulder |
| M25.522 | Pain in left elbow | Use for localized elbow pain |
| M25.532 | Pain in left forearm | Use for localized forearm pain |
| R07.9 | Chest pain, unspecified | Use when arm pain is related to or documented with cardiac symptoms |
When the provider establishes a definitive diagnosis (e.g., fracture, neuropathy, or cardiac condition), coders should avoid using left arm pain ICD 10 code as a standalone.
When to Use and When Not to Use
Use the left arm pain ICD 10 code (M79.602) when:
- The provider documents left arm pain without a confirmed underlying diagnosis.
- Pain is the primary reason for encounter and further evaluation is pending.
- Symptoms are nonspecific but require medical attention and billing justification.
Do not use when:
- A specific diagnosis explains the pain (fracture, sprain, tendinopathy, nerve injury).
- The documentation specifies pain in another location (e.g., shoulder, elbow, wrist).
- The payer requires a more definitive diagnosis for coverage.
Related CPT Codes with Left Arm Pain ICD-10 Code
The left arm pain ICD 10 code often pairs with diagnostic and therapeutic CPT codes, including:
| CPT Code | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| 73090 | X-ray, forearm | Ordered when pain is localized to the forearm and fracture needs to be ruled out |
| 73080 | X-ray, elbow, complete | Used when left arm pain is documented in the elbow region |
| 73110 | X-ray, wrist, complete | For left arm pain associated with wrist injuries or pathology |
| 97110 | Therapeutic exercise, per 15 minutes | Applied when therapy exercises are provided to address pain and restore function |
| 97140 | Manual therapy techniques, per 15 minutes | Used for manual mobilization or soft-tissue techniques to treat left arm pain |
| 99213 / 99214 | Evaluation & Management (E/M) visits | Commonly billed when the patient is evaluated for left arm pain during an office visit |
Proper pairing of M79.602 with these CPTs supports medical necessity and reduces claim edits.
Why Claims with Left Arm Pain ICD 10 Code Get Denied
One of the most frequent challenges providers face when billing the left arm pain ICD 10 code (M79.602) is payer denials. These often occur when claims lack sufficient medical necessity, when the code is used without proper clinical justification, or when documentation fails to clearly outline the provider’s assessment. Even a simple oversight like selecting the wrong laterality can result in claim rejection.
Denials are also common when M79.602 is billed as a standalone diagnosis despite the presence of a more definitive condition, such as a fracture or neuropathy. Payers expect coders to report the most specific diagnosis available, supported by detailed exam findings and time-based documentation. Without this, claims risk being flagged for medical review, delayed, or denied outright.
Denial Reasons and How to Prevent Them (M79.602 – Left Arm Pain ICD-10 Code)
| Denial Reason | Why It Happens | How to Prevent It |
|---|---|---|
| Lack of medical necessity | Provider notes do not justify why the service was required | Document detailed history, exam findings, and patient symptoms supporting medical need |
| Standalone diagnosis misuse | M79.602 used when a more definitive diagnosis (e.g., fracture, neuropathy) was already confirmed |
Always code the specific underlying condition if identified |
| Incorrect laterality | M79.601 (right arm) or unspecified codes used instead of M79.602 |
Double-check laterality in provider notes before claim submission |
| Insufficient documentation | Missing start/stop times, vague “arm pain” notes, or lack of clinical detail | Record exact minutes, location of pain, interventions performed, and patient response |
| Payer policy mismatch | Some payers require more specific diagnostic codes for approval | Verify payer-specific LCD / NCD or commercial coverage guidelines before billing |
What to Document
Coders and providers should document the following when using the left arm pain ICD 10 code:
- Location of pain (general arm vs. forearm, elbow, shoulder)
- Onset and duration (acute, chronic, post-traumatic)
- Associated symptoms (numbness, swelling, radiation, chest pain)
- Interventions performed (diagnostics, therapy, E/M visit details)
- Medical necessity rationale
Clear and precise notes protect providers during audits and strengthen billing compliance.
How Pro-MBS Can Help
We focus on precise ICD-10 and CPT coding for pain-related conditions, including the left arm pain ICD 10 code (M79.602). Our billing specialists apply payer-specific guidelines, ensure accurate code selection, and align documentation with compliance standards to minimize errors. This approach helps practices submit cleaner claims that stand up under audits.
By working with Pro-MBS, providers can significantly lower denial rates, accelerate reimbursements, and maintain compliance without the administrative burden. We integrate seamlessly with EHR systems, allowing practices to concentrate on delivering quality care while we manage the complexity of coding and billing requirements.




