In medical billing, revenue cycle accuracy is the backbone of successful reimbursements. One of the most misunderstood yet vital elements is the revenue code in medical billing. Providers, coders, and billers must know how revenue codes work because they directly connect services to payment. Misusing or omitting them often results in denials, underpayments, or compliance issues.
What Is a Revenue Code in Medical Billing?
A revenue code in medical billing is a four-digit numeric code reported on the UB-04 (CMS-1450) institutional claim form. It identifies the specific department, unit, or type of service that rendered care such as emergency room, laboratory, or pharmacy and enables payers to classify and reimburse claims accurately. For example, revenue code 0450 denotes Emergency Room services, distinct from similar procedures performed in different settings.
These codes are maintained by the National Uniform Billing Committee (NUBC), which ensures standardization across all institutional claims in the U.S.
Why Revenue Codes Matter
Revenue codes group similar services into organized line items on UB-04 claims so payers can process them efficiently. Without these codes, insurers may reject claims due to lack of service clarity. The revenue code complements CPT or HCPCS procedure codes by adding context around where the service took place such as the difference between a blood draw done in the emergency room (0450) versus in a treatment room (0761), which may influence reimbursement.
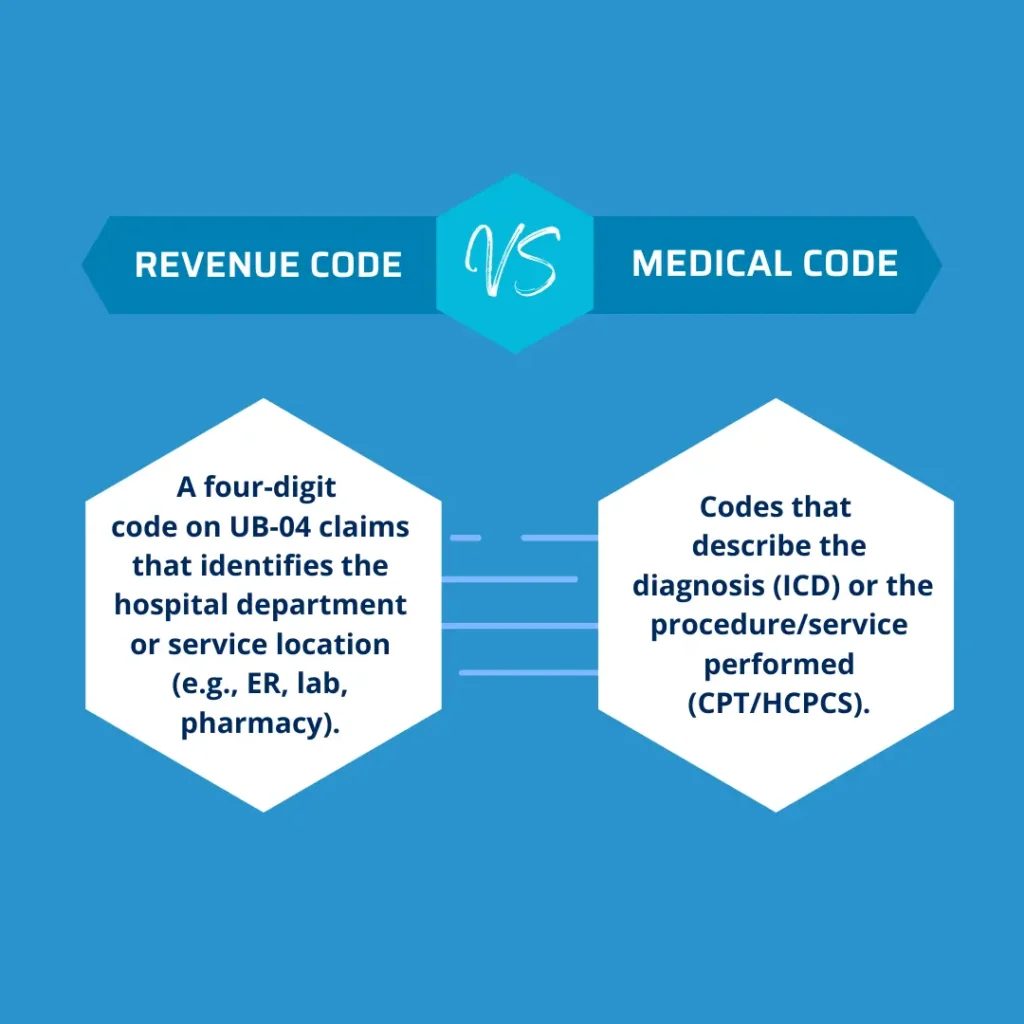
Revenue Code vs. Medical Code (ICD & CPT)
| Aspect | Revenue Code | Medical Code (ICD/CPT/HCPCS) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identifies hospital department/service | Identifies diagnosis (ICD) or procedure/service (CPT/HCPCS) |
| Format | Four-digit numeric code (e.g., 0450, 0300) | ICD-10 = alphanumeric (e.g., I10), CPT = 5 digits (e.g., 99213) |
| Claim Form | UB-04 (Institutional Billing) | CMS-1500 or UB-04 |
| Example | 0300 = Laboratory | 80053 = CMP blood test |
Why Claims with ICD 10 Code for Weight Loss Get Denied
Structure of Revenue Codes
A revenue code in medical billing follows a four-digit structure:
First Digit (0–9): Indicates accommodation (room/board) or ancillary services.
Middle Digits: Specify the service type (e.g., lab, radiology, ER).
Last Digit: Adds specificity or identifies subcategories.
Example:
0300 = Laboratory, General Classification
0301 = Laboratory, Hematology
0302 = Laboratory, Chemistry
Revenue Codes Used in Different Healthcare Settings

Revenue Codes for Emergency Room Visits
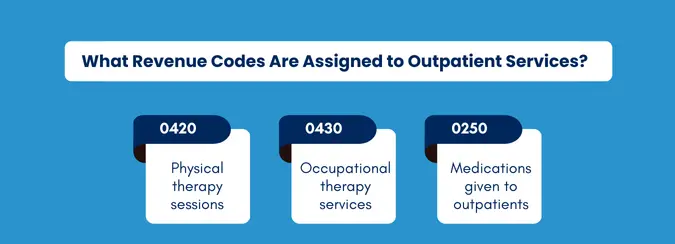
Revenue Codes for Outpatient Services

Revenue Codes for Intensive Care Unit (ICU)
ICU revenue codes are designed to reflect the level and type of critical care provided. 0200 is the general code for comprehensive ICU services, while 0201 is specifically for post-surgical ICU care following major procedures. 0206 applies to step-down or intermediate ICU services, which are less intensive than full critical care but more than standard medical-surgical floors. 0207 is dedicated to burn ICU services, which require specialized equipment and care teams. Using the correct ICU codes ensures accurate reimbursement for these high-cost, resource-intensive services.

Revenue Codes for Pharmacy
Pharmacy revenue codes capture the costs of medications dispensed during care. 0250 applies broadly to general pharmacy charges, including most inpatient and outpatient drugs. 0256 is used for investigational or trial medications, often part of clinical studies. 0257 refers to over-the-counter drugs provided to patients. 0258 is applied to IV fluids and related pharmaceutical products. These codes allow hospitals and clinics to bill medications accurately, ensuring both compliance and reimbursement for pharmacy services.

Revenue Codes for Inpatient Services
Inpatient revenue codes cover the costs of hospital stays and related procedures. 0120 is for semi-private rooms, where two patients share accommodation. 0360 represents operating room services, capturing the costs of surgical procedures and related resources. 0250 can also be applied here for medications given during an inpatient stay. By assigning these codes properly, hospitals ensure that all aspects of inpatient care from room charges to surgical services are correctly documented and billed.
Why Revenue Codes Are Essential for Providers
1. Ensure Accurate Payment
2. Support Audits & Compliance
In today’s compliance-driven healthcare environment, payers and regulatory bodies such as CMS require transparency in billing. Revenue codes create a clear audit trail that connects the service delivered, the department that performed it, and the charges applied. This detailed mapping helps providers pass payer audits, avoid penalties, and demonstrate compliance with federal and state regulations, reducing legal and financial risk.
3. Improve Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) Efficiency
Revenue cycle teams rely on precise revenue codes to streamline claims processing and reporting. When revenue codes align properly with CPT/HCPCS and ICD-10 codes, it minimizes back-and-forth with insurers and reduces the chances of claim rework. This efficiency leads to faster reimbursements, reduced accounts receivable days, and stronger overall cash flow are key outcomes for sustainable practice management.
4. Link Services to Departments
Conclusion
Revenue codes are more than just billing identifiers, they are the bridge between clinical care, financial reimbursement, and regulatory compliance. In 2025’s increasingly complex healthcare environment, accurate use of revenue codes ensures that every service is correctly tied to its department, appropriately reimbursed, and fully transparent for audits. By linking revenue codes with ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS, providers can create a complete and compliant claim narrative that reduces denials, accelerates payments, and strengthens revenue cycle performance.
For healthcare organizations, mastering revenue codes is not just about avoiding errors, it is about building financial integrity and operational clarity. Whether in the ER, ICU, pharmacy, or outpatient services, precise coding empowers providers to safeguard compliance, optimize reimbursement, and support better decision-making. In short, revenue codes remain a cornerstone of effective revenue cycle management and sustainable healthcare delivery.



