Top 10 ICD 10 Codes in Primary Care: Detailed Guide for Beginners
If you're new to medical billing and coding, understanding ICD-10 codes can feel overwhelming. But these codes play a crucial role in healthcare: from patient documentation to insurance reimbursement and claims accuracy.
In this guide, we’ll explore the most frequently used ICD-10 codes in primary care based on 2025 data. For each, you’ll learn what it means, when to use it, and why it matters for medical billing, compliance, and patient care.
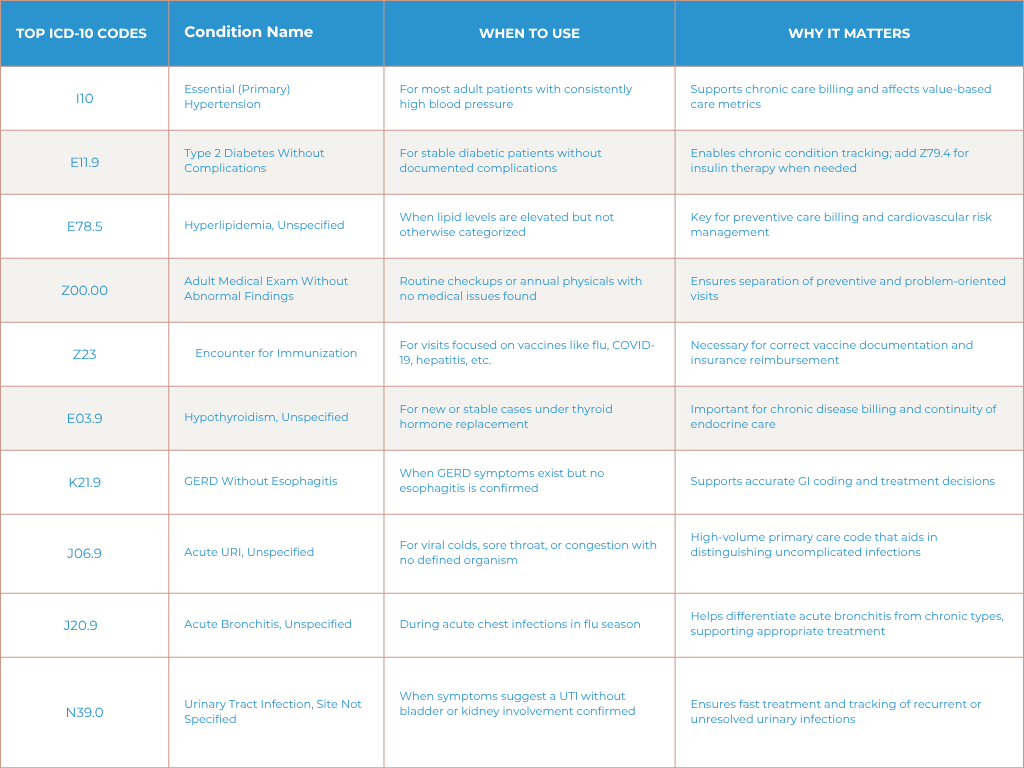
1. I10 – Essential (Primary) Hypertension
What it is: High blood pressure not caused by another condition.
When to use it: For most adult patients with persistent elevated blood pressure.
Why it matters: Proper ICD-10 coding for hypertension supports chronic care management and clean claims submission. Accurate diagnosis codes also influence performance metrics in value based care.
2. E11.9 – Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Without Complications
What it is: Type 2 diabetes with no noted complications such as neuropathy or nephropathy.
When to use it: For patients who are stable on medication and have no diabetes related conditions.
Why it matters: Correct coding is essential for chronic condition tracking and insurance reimbursement. Don’t forget to also add Z79.4 for long term insulin use if applicable.
3. E78.5 – Hyperlipidemia, Unspecified
What it is: Elevated cholesterol or lipids, not otherwise specified.
When to use it: When lab results show abnormal lipid levels without further detail.
Why it matters: Capturing lipid disorders is essential in preventive care coding and helps guide treatment for cardiovascular risk reduction.
4. Z00.00 – General Adult Medical Examination Without Abnormal Findings
What it is: A routine adult check-up where no issues are discovered.
When to use it: For wellness visits or annual physicals that are problem free.
Why it matters: This code ensures preventive services billing is separated from problem-oriented visits, improving claim accuracy and insurance coverage.
5. Z23 – Encounter for Immunization
What it is: Visit primarily for the administration of vaccines.
When to use it: Flu shots, COVID-19 vaccines, hepatitis, or childhood immunizations.
Why it matters: Immunization visits should be coded separately to ensure correct claim processing and public health documentation.
6. E03.9 – Hypothyroidism, Unspecified
What it is: Underactive thyroid function without a specified cause.
When to use it: When hypothyroidism is newly diagnosed or the patient is stable and under treatment.
Why it matters: Supports chronic condition coding and justifies ongoing thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
7. K21.9 – GERD Without Esophagitis
What it is: Gastroesophageal reflux symptoms such as heartburn or acid reflux without esophageal inflammation.
When to use it: When patients present with GERD symptoms but endoscopy does not show esophagitis.
Why it matters: Proper coding ensures accurate billing for digestive disorders and guides long term management.
8. J06.9 – Acute Upper Respiratory Infection, Unspecified
What it is: A common cold or viral infection affecting the upper respiratory tract.
When to use it: During acute visits for cough, sore throat, or nasal symptoms.
Why it matters: A high volume primary care code that helps distinguish uncomplicated colds from more severe respiratory conditions.
9. J20.9 – Acute Bronchitis, Unspecified
What it is: Temporary inflammation of the bronchial tubes without a known cause.
When to use it: Seen frequently during flu season for patients with chest congestion and coughing.
Why it matters: Helps differentiate from chronic bronchitis and guides treatment for acute respiratory issues.
10. N39.0 – Urinary Tract Infection, Site Not Specified
What it is: UTI without specifying location such as bladder or kidney.
When to use it: For patients with urinary symptoms but no confirmed localization.
Why it matters: UTI coding supports quick treatment, follow-up, and helps monitor recurrent infections.
Why These ICD-10 Codes Matter in Medical Billing and Coding
These codes are essential for daily operations in primary care. They ensure accurate billing, documentation, and communication with insurance providers. Proper use of ICD-10 codes helps:
- Prevent claim rejections and denials
- Support chronic care management
- Meet value-based care goals
- Improve patient tracking and reporting
- Enhance clinical documentation integrity
Coding accuracy also impacts your performance in CMS programs such as MIPS and HEDIS. With correct diagnosis coding, your practice can avoid audits, speed up reimbursement, and improve patient care.
Tips for Using ICD-10 Codes Correctly
To use ICD-10 codes effectively:
- Document thoroughly in the patient record
- Select the most specific code available
- Use Z-codes for screenings, vaccinations, and follow-ups
- Stay current with annual ICD-10 updates
- Train all staff involved in billing and coding
- Use EHR tools to streamline and cross-reference codes
Final Thoughts
Mastering the top ICD-10 codes in primary care is essential for smooth billing, accurate claims, and high quality care. From hypertension and diabetes to UTIs and respiratory infections, these codes reflect the most common reasons patients visit your clinic.
Staying up-to-date with annual changes and training your team are key to long-term success. Continue learning, follow documentation best practices, and use smart technology to support your medical billing and coding efforts in 2025 and beyond. Get a free consultation with PROMBS today and let our experts help you stay ahead of audits, denials, and documentation errors.




